
4 innovative uses of BIM, episode 3: BIM for a controlled building project
4 minutes of reading
Exchanging information so that all stakeholders share a common vision of the project: welcome to the BIM era! Every week, you can learn about one project where BIM is being used innovatively. Today we will look at L’Oréal’s L6 building by Bouygues Energies & Services.
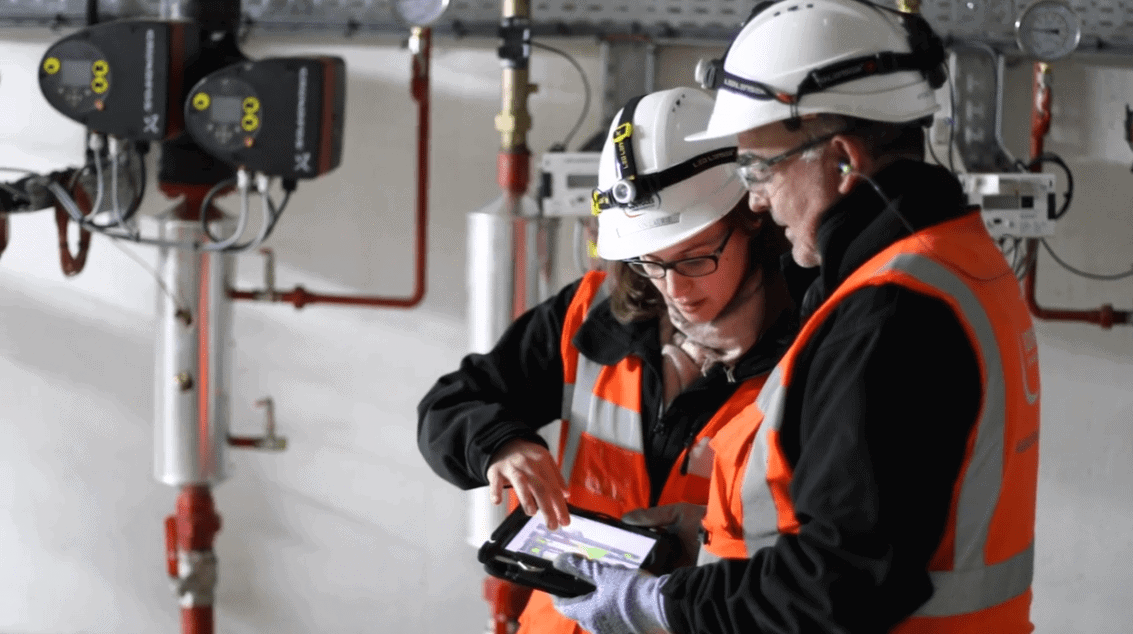

A number of laboratory buildings have already been constructed for L’Oréal’s cosmetics research centre (L1, L2, L3, etc.). This new project, ‘L6’, is part of the company’s strategy to bring together teams of researchers on campus, and was built in collaboration with these teams with the help of BIM and virtual reality.
The building, which measures 5,300 m², was handed over in June 2018. The building is distributed over a ground floor, three upper floors and a basement specifically for technical facilities. An underground tunnel and an overhead tunnel connect the building to the adjacent L4 laboratory. The roof houses a terrace fitted with photovoltaic solar panels. The project was conceived to have a modular design and to provide flexibility of use for incoming teams, whilst allowing for a long-term, scalable use of the premises, with the ability to incorporate a variety of different functions as needed. Bouygues Energies & Services produced the air-conditioning, ventilation, special fluids and plumbing lots.
 Collaborating with future users
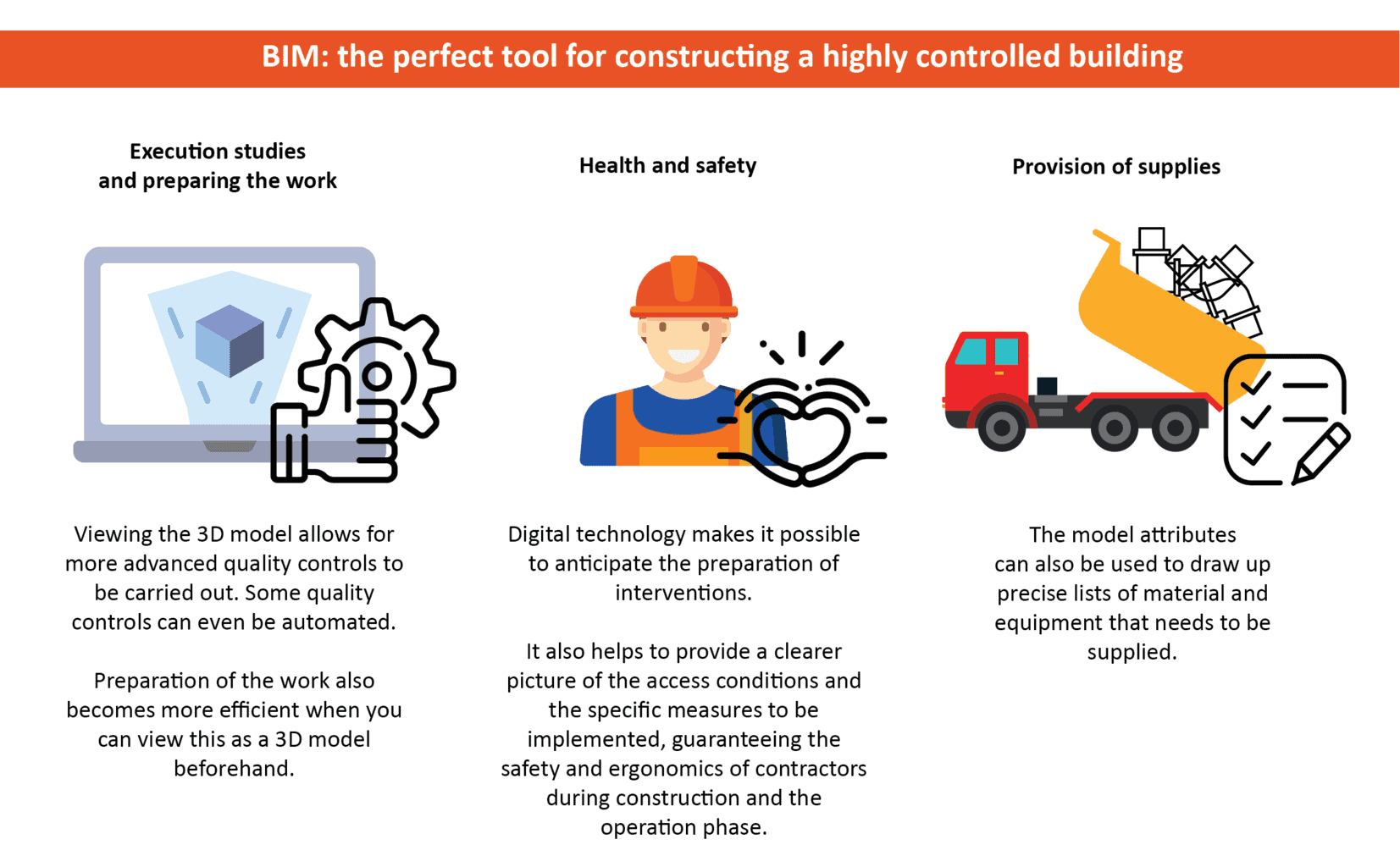
As the project owner, L’Oréal was in favour of setting up innovative and interactive solutions to design and build the spaces. With the help of BIM and virtual reality, future users of the building were able to immerse themselves in their prospective working environment from as early as the design phase, using 3D modelling of the flexible laboratories, support laboratories and traffic flows. Thanks to the commitment of the project teams, Bouygues Energies & Services participated in the co-construction process, including in the execution studies, supervision, management, HVACE and development which, as each of these areas became involved in the process, added attributes to the model pertaining to our technical facilities, networks, diagrams, notices and commissioning data, via standard tools (Office Excel), and our digital commissioning tool, Resolving.
Finally, by using their tools, L’OREAL was able to incorporate relevant maintenance/operating data from the up-to-date model. The true meaning of shared innovation!
Collaborating with future users
As the project owner, L’Oréal was in favour of setting up innovative and interactive solutions to design and build the spaces. With the help of BIM and virtual reality, future users of the building were able to immerse themselves in their prospective working environment from as early as the design phase, using 3D modelling of the flexible laboratories, support laboratories and traffic flows. Thanks to the commitment of the project teams, Bouygues Energies & Services participated in the co-construction process, including in the execution studies, supervision, management, HVACE and development which, as each of these areas became involved in the process, added attributes to the model pertaining to our technical facilities, networks, diagrams, notices and commissioning data, via standard tools (Office Excel), and our digital commissioning tool, Resolving.
Finally, by using their tools, L’OREAL was able to incorporate relevant maintenance/operating data from the up-to-date model. The true meaning of shared innovation!
 Collaborating with other building trades
The concept of collaboration was also key between the different building trades and stakeholders involved in the project. From the tender documents, the project owner set out several requirements that were tied to the construction of the building, including the requirement to use a BIM-integrated approach from the design to integration in operations, and the BEPOS (positive-energy building) experimental environmental certification. The digital model had to be compatible with asset management software and operating systems (ABYLA and CARLSOURCE). This was with a view to anticipate the preparation of interventions.
Collaborating with other building trades
The concept of collaboration was also key between the different building trades and stakeholders involved in the project. From the tender documents, the project owner set out several requirements that were tied to the construction of the building, including the requirement to use a BIM-integrated approach from the design to integration in operations, and the BEPOS (positive-energy building) experimental environmental certification. The digital model had to be compatible with asset management software and operating systems (ABYLA and CARLSOURCE). This was with a view to anticipate the preparation of interventions.

 Collaborating with future users
As the project owner, L’Oréal was in favour of setting up innovative and interactive solutions to design and build the spaces. With the help of BIM and virtual reality, future users of the building were able to immerse themselves in their prospective working environment from as early as the design phase, using 3D modelling of the flexible laboratories, support laboratories and traffic flows. Thanks to the commitment of the project teams, Bouygues Energies & Services participated in the co-construction process, including in the execution studies, supervision, management, HVACE and development which, as each of these areas became involved in the process, added attributes to the model pertaining to our technical facilities, networks, diagrams, notices and commissioning data, via standard tools (Office Excel), and our digital commissioning tool, Resolving.
Finally, by using their tools, L’OREAL was able to incorporate relevant maintenance/operating data from the up-to-date model. The true meaning of shared innovation!
Collaborating with future users
As the project owner, L’Oréal was in favour of setting up innovative and interactive solutions to design and build the spaces. With the help of BIM and virtual reality, future users of the building were able to immerse themselves in their prospective working environment from as early as the design phase, using 3D modelling of the flexible laboratories, support laboratories and traffic flows. Thanks to the commitment of the project teams, Bouygues Energies & Services participated in the co-construction process, including in the execution studies, supervision, management, HVACE and development which, as each of these areas became involved in the process, added attributes to the model pertaining to our technical facilities, networks, diagrams, notices and commissioning data, via standard tools (Office Excel), and our digital commissioning tool, Resolving.
Finally, by using their tools, L’OREAL was able to incorporate relevant maintenance/operating data from the up-to-date model. The true meaning of shared innovation!
 Collaborating with other building trades
The concept of collaboration was also key between the different building trades and stakeholders involved in the project. From the tender documents, the project owner set out several requirements that were tied to the construction of the building, including the requirement to use a BIM-integrated approach from the design to integration in operations, and the BEPOS (positive-energy building) experimental environmental certification. The digital model had to be compatible with asset management software and operating systems (ABYLA and CARLSOURCE). This was with a view to anticipate the preparation of interventions.
Collaborating with other building trades
The concept of collaboration was also key between the different building trades and stakeholders involved in the project. From the tender documents, the project owner set out several requirements that were tied to the construction of the building, including the requirement to use a BIM-integrated approach from the design to integration in operations, and the BEPOS (positive-energy building) experimental environmental certification. The digital model had to be compatible with asset management software and operating systems (ABYLA and CARLSOURCE). This was with a view to anticipate the preparation of interventions.

More reading
Read also



What lies ahead? 7 megatrends and their influence on construction, real estate and urban development
Article
20 minutes of reading

