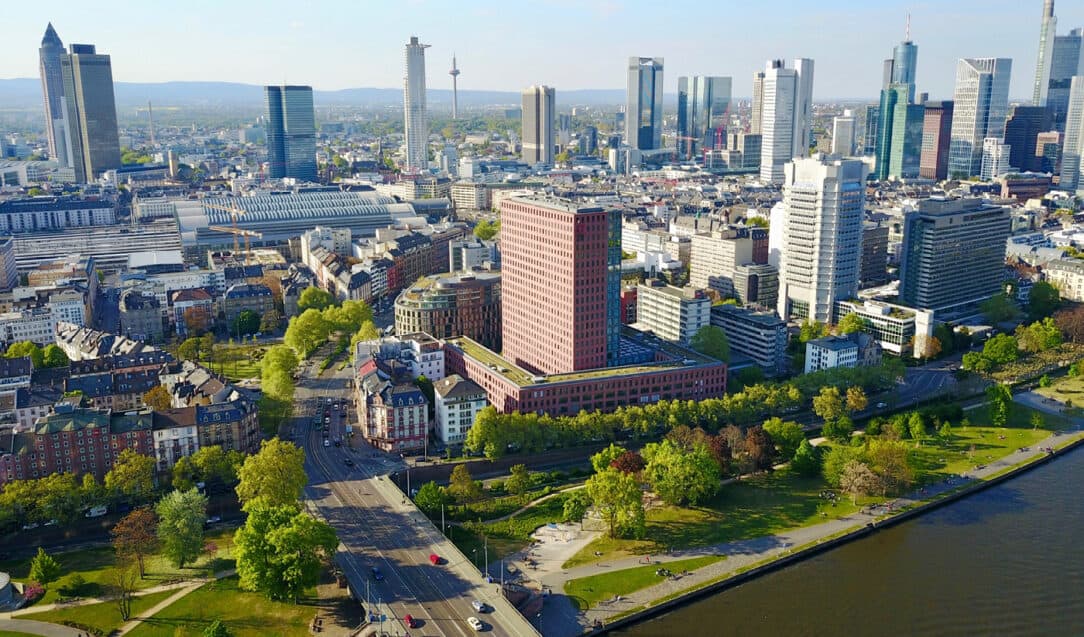
Fibre optic – a way to increase the attractiveness and development of regions
By 2025, the entire metropolitan area will be connected to fibre-optic cable. This rollout is eagerly awaited in rural and suburban areas. This would result in a positive impact on the local economy.
Urban farming: how Monaco reconnects the city to the environment
Urban vegetable gardens have been appearing in Monaco since 2016. A concept called "Terre de Monaco" extends over 1,600 m2 of ground and roof space. It’s a real breath of fresh air for the Principality which is 80% concrete! Interview with… Jessica Sbaraglia, founder of Terre de Monaco
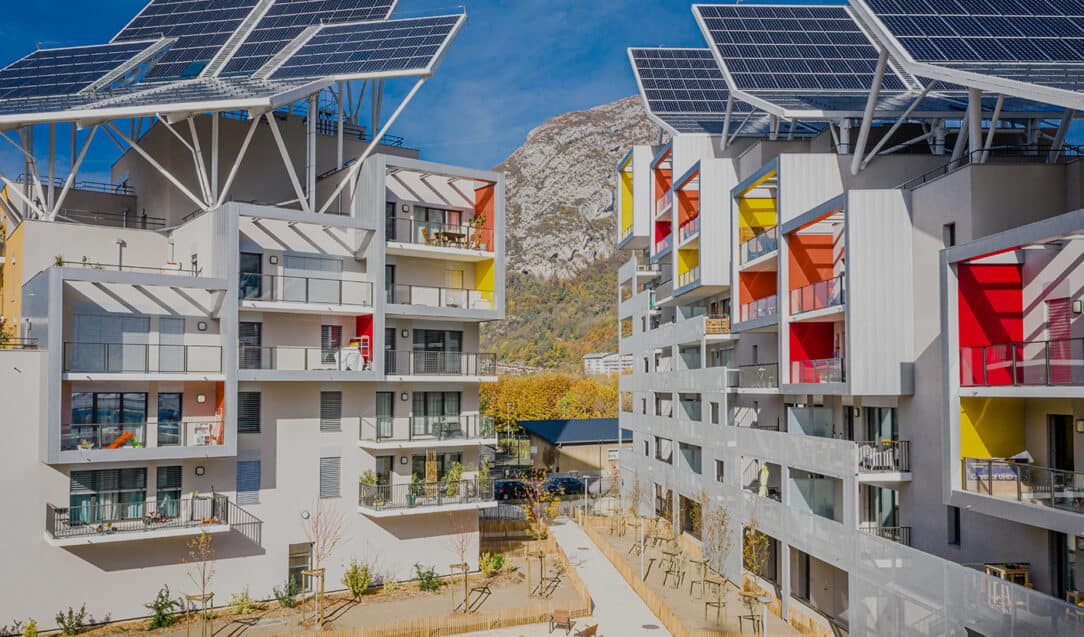
New construction methods : towards sustainable buildings
Bouygues Construction unveils three innovative sustainable building projects: an autonomous building in Grenoble, a fertile island in Paris and a sustainable district in Sevran.
Generative design: when AI designs our living spaces
What if tomorrow, our living spaces were designed to precisely match our needs based on the best possible layout—one created by a computer?
What is the link between buildings and mobility?
In theory, there is none ... The world of mobility is changing and is no longer limited to transport.
What if tomorrow nanotechnologies were to bring about a revolution in the building industry?
Nanotechnologies include manufacturing techniques and processes in the microscopic world. Outlook for the building industry.
How do you see your housing?
We interviewed 1,000 young people about their housing. Their answers were very enlightening!
Risk mapping: a decision-making and anticipation tool
Interview with Alexia Fakiri, Internal Control Manager at Bouygues Construction.
The tertiary decree: 60% energy savings are in sight
The so-called ‘tertiary’ decree, applicable since 2019, imposes a gradual reduction in the energy consumption of this type of building up until 2050. Like any new regulation, this involves a period of adaptation - especially as the objectives set are ambitious. However, the ‘Syndicat professionnel des entreprises de la transition énergétique et numérique’ (Serce) (Professional Union of Energy and Digital Transition Companies)considers them to befully attainable.
“Observe nature, for it is where your future lies”
Leonardo da Vinci. This quote could be the motto of biomimicry. What does that mean for the real estate sector? Bio-based real estate: reinventing a city by living organisms, for living organisms. Pauline Philippe tell us more.